| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
21c. Bipolar Line Encoding | Next |
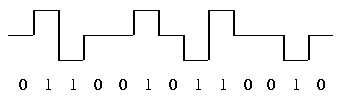
Bipolar Line Encoding
Synchronization of receive and transmit clocks is greatly improved except if there is a long string of 0s transmitted. Bipolar line encoding is also called Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI).
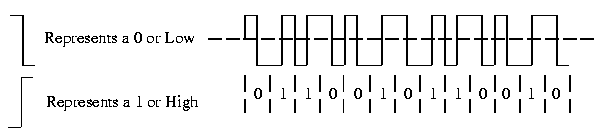
Manchester line encoding has no DC component and there is always a transition available for synchronizing receive and transmit clocks. Manchester line encoding is also called a self clocking line encoding. It has the added benefit of requiring the least amount of bandwidth compared to the other line encoding. Manchester line encoding requires 2 frequencies: the base carrier and 2 x the carrier frequency. All others require a range from 0 hertz to the maximum transfer rate frequency.
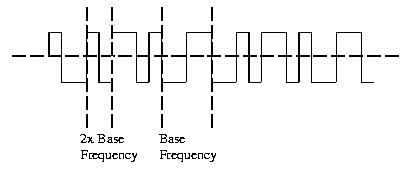
Manchester line encoding can detect errors during transmission. a transition is expected for during every bit period. The absence of a transition would indicate an error condition.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |