| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
21b. Polar Encoding | Next |
There is still a small residual DC problem but Polar line encoding is a great improvement over Unipolar line encoding. Polar encoding has an added benefit in that it reduces the power required to transmit the signal by one-half compared with unipolar.
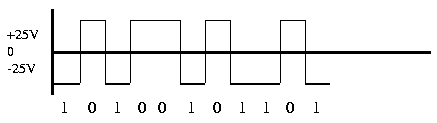
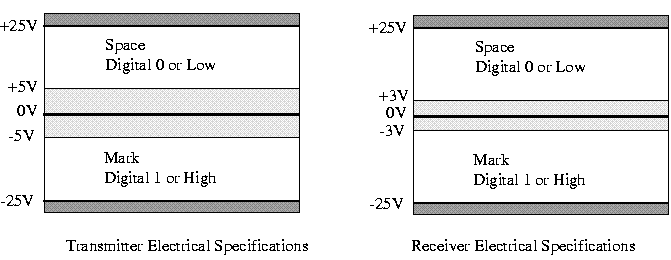
RS-232D TXD
Polar line encoding has the same synchronization problem as Unipolar line encoding. If there is a long string of logical 1s or 0s, the receive oscillator may drift and become unsynchronized.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |