| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
15d. Optical Fibre (cont'd) | Next |
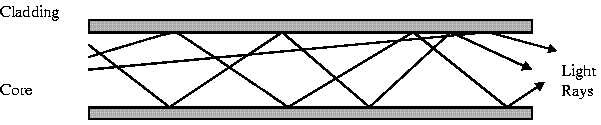
Grade Index has a gradual change in the Core's Refractive Index. This causes the light rays to be gradually bent back into the core path. This is represented by a curved reflective path in the attached drawing. The result is a better receive signal than Step Index. LED light sources are used. Typical Core: 62.5 microns.
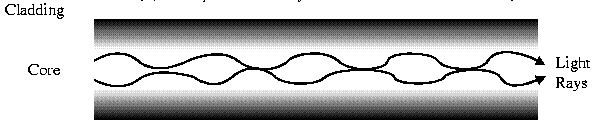
Note: Both Step Index and Graded Index allow more than one light source to be used (different colours simultaneously!). Multiple channels of data can be run simultaneously!
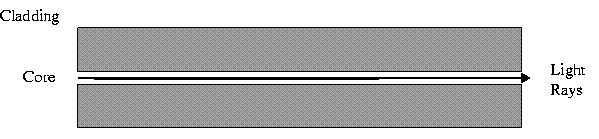
Single Mode has separate distinct Refractive Indexes for the cladding and core. The light ray passes through the core with relatively few reflections off the cladding. Single Mode is used for a single source of light (one colour) operation. It requires a laser and the core is very small: 9 microns.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |