| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
36f. MAC - Medium Access Control (cont'd) | Next |
Indicates the destination (receiving station) of the frame. It can be 2 or 6 octets long (16 or 48 bits), usually it is 6 octets (the 2 octet version is used for compatibility with the original Ethernet frame from XNS and is considered obsolete).
The DA field consists of
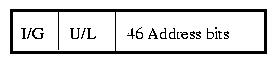
I/G stands for Individual/Group. It indicates whether the destination is for an individual or for a multicast broadcast. It is one bit long:
A multicast broadcast can be for everyone or for a group. For a multicast broadcast to all stations, the Destination Address = FFFFFFFFFFFFh (h - hexadecimal notation). To multicast to a specific group, unique addresses must be assigned to each station by the Network Administrator.
U/L stands for Universal/Local. It allows for unique addresses. It is used to indicate whether a local naming convention is used - administered by the Network Administrator (not recommended - incredible amount of work) or the burnt-in ROM address is used (recommended).
The 46 Bit Address Field consists of 46 bits indicating the destination NIC cards address burnt into the firmware (ROM) of the card or the unique name assigned to the card during the card's initialization by the Network Administrator.
Source Address (SA)
The Source Address indicates the source or transmitting station of the frame. It is identical in format to the Destination Address but always has the I/G bit = 0 (Individual/Group Bit = Individual)
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |